How To Grow High Yield Tomato Plants: 50-80 lbs per Plant

Make sure to like Living Green and Frugally on Facebook, Shop at Amazon to help support my site and explore our PINTEREST BOARDS for innovative ways you can become self-sufficient.
Growing high-yield tomato plants, capable of producing 50-80 pounds of fruit per plant, requires a combination of selecting the right variety, providing optimal growing conditions, and adhering to proper care techniques. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you achieve this impressive yield.
1. Choose the Right Tomato Variety
High-yield varieties are crucial for achieving a significant harvest. Some of the best varieties for high yields include:
- Beefsteak Tomatoes: Known for their large size and heavy production.
- Roma Tomatoes: Prolific producers, ideal for sauces and canning.
- Cherry and Grape Tomatoes: These small varieties often produce abundant fruit.
- Hybrid Varieties: Varieties like ‘Big Boy,’ ‘Better Boy,’ and ‘Celebrity’ are bred for high yields and disease resistance.
2. Start with Healthy Seedlings
Healthy seedlings are the foundation of productive plants. Here’s how to ensure you start off right:
- Seed Starting: Begin seeds indoors 6-8 weeks before the last frost date. Use a high-quality seed-starting mix.
- Transplanting: Harden off seedlings by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions before planting them in the garden.
3. Soil Preparation
Tomatoes thrive in well-draining, nutrient-rich soil. Preparing the soil correctly can make a significant difference:
- pH Level: Aim for a soil pH between 6.0 and 6.8.
- Amendments: Incorporate compost, well-rotted manure, and organic matter to enrich the soil. Add lime if the soil is too acidic.
- Drainage: Ensure good drainage to prevent root rot.
View this post on Instagram
4. Planting Techniques
Proper planting techniques can help your tomato plants thrive:
- Spacing: Space plants 24-36 inches apart to allow for adequate airflow and reduce disease risk.
- Depth: Plant seedlings deep, burying two-thirds of the stem to encourage a robust root system.
- Support: Use stakes, cages, or trellises to support the plants and keep fruits off the ground.
5. Watering Practices
Consistent and appropriate watering is essential for high yields:
- Frequency: Water deeply and consistently, about 1-2 inches per week. Adjust based on weather conditions.
- Timing: Water in the morning to reduce evaporation and prevent fungal diseases.
- Method: Use drip irrigation or a soaker hose to deliver water directly to the roots.
6. Fertilization
Feeding your tomato plants properly can boost their productivity:
- Balanced Fertilizer: Use a balanced fertilizer with equal parts nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (e.g., 10-10-10).
- Side-Dressing: Apply a side-dressing of compost or fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season.
- Calcium: Add calcium to prevent blossom-end rot, using gypsum or crushed eggshells.
7. Pruning and Training
Pruning and training tomato plants can lead to higher yields:
- Remove Suckers: Prune suckers (the small shoots that grow in the leaf axils) to direct the plant’s energy into producing fruit.
- Prune Lower Leaves: Remove the lower leaves to improve air circulation and reduce disease risk.
- Training: Train plants to a single or double stem system for better light penetration and easier management.
8. Pest and Disease Management
Keeping your plants healthy and free from pests and diseases is crucial:
- Mulching: Use mulch to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and prevent soil-borne diseases.
- Companion Planting: Grow basil, marigold, and garlic nearby to repel pests.
- Organic Pesticides: Use neem oil or insecticidal soap to control pests like aphids and whiteflies.
- Disease-Resistant Varieties: Choose disease-resistant varieties to reduce the risk of common tomato diseases.
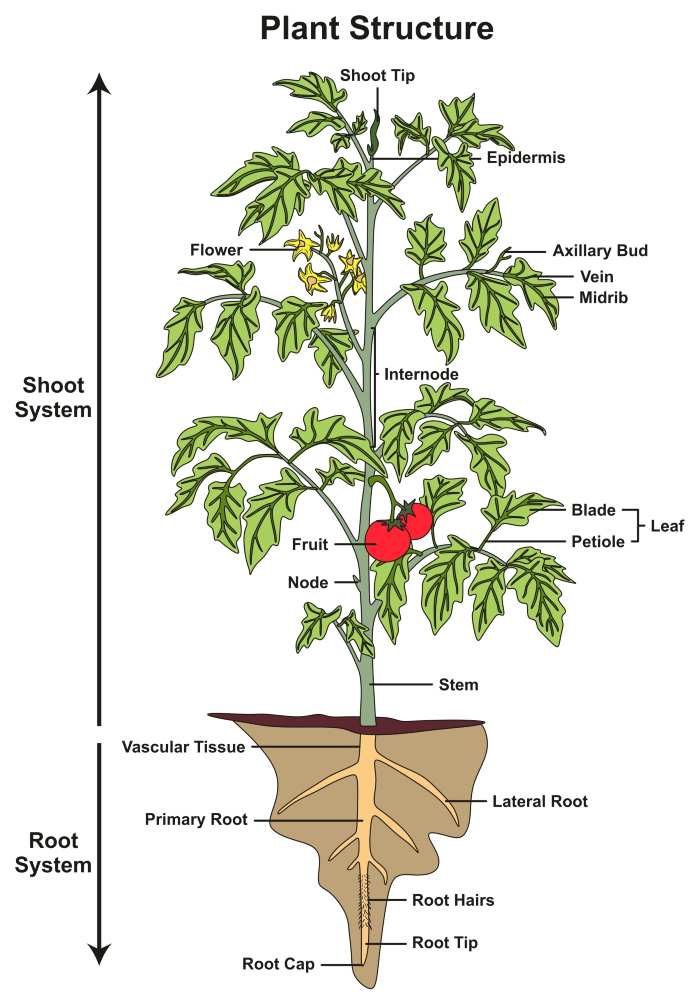
9. Harvesting
Proper harvesting techniques ensure the best quality fruit:
- Timing: Harvest tomatoes when they are fully ripe for the best flavor. For high yields, regularly pick fruits to encourage more production.
- Method: Use a gentle twisting motion to remove tomatoes from the vine to avoid damaging the plant.
10. Continuous Learning
Stay informed and adapt your gardening practices:
- Research: Stay updated with the latest gardening techniques and tomato varieties.
- Experimentation: Try different methods and varieties to see what works best in your specific growing conditions.
By following these steps and paying attention to the needs of your tomato plants, you can achieve impressive yields of 50-80 pounds per plant. Happy gardening!